
Table of Contents
A chronic ectopic pregnancy, also known as an abdominal ectopic pregnancy or a secondary abdominal pregnancy, is a rare and serious medical condition. In a normal pregnancy, a fertilised egg implants and grows in the uterus. However, in an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilised egg implants and begins to grow outside the uterus.
Most ectopic pregnancies occur in the Fallopian tubes, but in rare cases, they can occur in other locations in the abdomen.
A chronic ectopic pregnancy is different from a typical ectopic pregnancy in that it has a longer duration and may be associated with different symptoms.
Some of the key characteristics and features of a chronic ectopic pregnancy include:
- Delayed diagnosis: Chronic ectopic pregnancies are often not diagnosed as quickly as typical ectopic pregnancies. This is because the symptoms may be less severe, and the pregnancy may continue for a longer period.
- Vague symptoms: Symptoms of a chronic ectopic pregnancy can be vague and nonspecific, including abdominal pain, pelvic pain, and irregular vaginal bleeding.
- Growth in the abdomen: In a chronic ectopic pregnancy, the fertilised egg continues to grow outside the uterus, often in the abdominal cavity. This can lead to the development of a mass or lump in the abdomen.
- Risk of rupture: As the pregnancy progresses, there is an increased risk of the ectopic pregnancy rupturing, which can cause severe internal bleeding and be life-threatening.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis of a chronic ectopic pregnancy typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, ultrasound imaging, and blood tests to measure pregnancy hormone levels (beta hCG).
- Treatment: Treatment options for a chronic ectopic pregnancy may include surgery to remove the ectopic pregnancy, which is often necessary to prevent rupture and serious complications. In some cases, medication may be used to stop the growth of the ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms:
Common symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may include:

- Abdominal Pain: One of the most common symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy is sharp, stabbing pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
The pain may come and go or be constant, and it may range from mild to severe. - Vaginal Bleeding: Ectopic pregnancies often cause vaginal bleeding that can be lighter or heavier than your normal menstrual period. The bleeding could be ongoing or sporadic.
- Shoulder or Neck Pain: If the ectopic pregnancy ruptures, it can cause internal bleeding, which may lead to referred pain in the shoulder or neck area. This pain can be a sign of a medical emergency.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some women with ectopic pregnancies experience nausea and vomiting, which can be attributed to the hormonal changes associated with pregnancy.
- Weakness and Dizziness: Internal bleeding from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can lead to a drop in blood pressure, causing weakness, light-headedness, or fainting.
- Rectal Pressure: In rare cases, an ectopic pregnancy can press against the rectum, causing discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the rectal area.
It’s important to note that not all women with an ectopic pregnancy will experience all of these symptoms, and symptoms can vary in intensity. Some women may have mild symptoms that they may mistake for a normal pregnancy or other gynaecological issues.
Types of ectopic pregnancy:
Ectopic pregnancies can occur in various locations outside the uterus. While the most common type is a tubal ectopic pregnancy, there are several less common types and locations for ectopic pregnancies.
Here are some of the types of ectopic pregnancies:
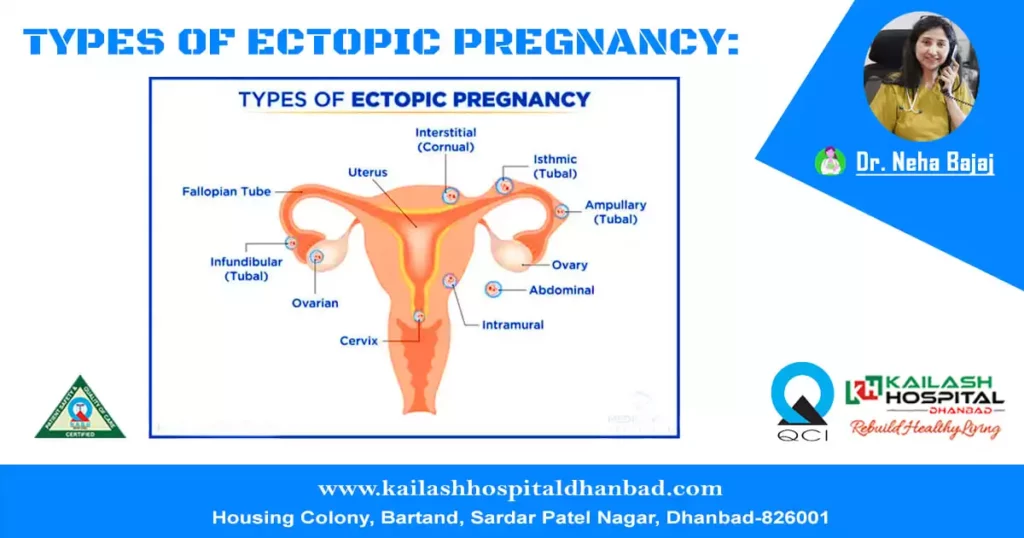
- Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy: This is the most common type of ectopic pregnancy, where the fertilized egg implants and begins to grow in one of the fallopian tubes. Over 90% of ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tubes.
- Cornual Ectopic Pregnancy: In a cornual ectopic pregnancy, the fertilised egg implants in one of the horns or corners of the uterus. This type is rare and can be more difficult to diagnose because it may appear similar to a normal intrauterine pregnancy.
- Interstitial Ectopic Pregnancy: Similar to cornual ectopic pregnancies, an interstitial ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants in the uterine horn but extends into the fallopian tube. This type is also relatively rare.
- Ovarian Ectopic Pregnancy: In an ovarian ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg attaches to the surface of one of the ovaries. This type is less common but can be challenging to diagnose.
- Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: In an abdominal ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and grows in the abdominal cavity, outside the uterus and fallopian tubes. This is a rare and dangerous type of ectopic pregnancy.
- Cervical Ectopic Pregnancy: A cervical ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus. This type can be associated with heavy bleeding and is relatively rare.
- Heterotopic Pregnancy: In a heterotopic pregnancy, there is both an ectopic pregnancy and a normal intrauterine pregnancy occurring simultaneously. This is a rare occurrence, more common in women who undergo fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy Variants: Within tubal ectopic pregnancies, there can be variations in the location of implantation, such as ampullary, isthmic, or fimbrial ectopic pregnancies, depending on which part of the fallopian tube is affected.
Food to prevent ectopic pregnancy:
Unfortunately, there are no specific foods or dietary changes that can prevent ectopic pregnancy. Such pregnancies are primarily caused by factors unrelated to diet or nutrition, such as issues with the Fallopian tubes, previous pelvic surgeries, or certain medical conditions.
To reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy, it’s essential to focus on overall reproductive health and preventive measures:

- Regular Medical Checkups: Routine gynaecological checkups can help detect and address any reproductive health issues early on.
- Safe Sex and Birth Control: Practicing safe sex and using effective birth control methods can reduce the risk of unintended pregnancies, which are more likely to result in ectopic pregnancies if they occur.
- Prompt Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Some STIs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can increase the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which, in turn, can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. The importance of early detection and treatment of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) cannot be overstated.
- Pelvic Health: Prioritize pelvic health and seek medical attention if you have symptoms like pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or other reproductive health concerns.
- Fertility Awareness: Understanding your menstrual cycle and fertility can help you time intercourse to increase the chances of conception in the uterus rather than the Fallopian tubes.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can harm reproductive health. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake may help maintain overall reproductive well-being.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and may indirectly support reproductive health.
In closing
It’s important to note that ectopic pregnancies are typically not viable, and the fertilized egg cannot develop into a healthy fetus. They pose serious risks to the health of the pregnant person and require prompt medical intervention, often involving surgical removal or medication to terminate the pregnancy.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications, such as Fallopian tube rupture and severe bleeding. Chronic ectopic pregnancies are extremely rare, and the majority of ectopic pregnancies are diagnosed and treated much earlier.
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy or are experiencing symptoms like abdominal pain and irregular bleeding, it’s essential to seek medical attention from a consultant gynaecology promptly, as early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes



